Javascript in the Browser - Git and GitHub Foundations
- Duration: 1 hour
Github, what is it?
At a high level, GitHub is a website and cloud-based service that helps developers store and manage their code, as well as track and control changes to their code. To understand exactly what GitHub is, you need to know two connected principles:
- Version control
- Git
What is Version Control?
Version control is the management of changes to documents, computer programs, websites, and other collections of information.
What is Git?
Git is a specific open-source version control system created in 2005 by Linus Torvalds, the creator of Linux. Specifically, Git is a distributed version control system, which means that the entire codebase and history is available on every developer’s computer. It can be used with any file type such as such as Unity projects or WebVR projects, but is most often used for tracking simple codebases.
GitHub is a Git repository hosting service. It allows developers and engineers to create remote, public-facing repositories on the cloud for free. While Git is a command line tool, GitHub provides a Web-based graphical interface.
For the following reasons, GitHub is the version control manager of choice:
- It manage changes over time.
- It aids sharing and collaboration.
- It allows for experimentation.
References: Getting Started with GitHub Desktop, GitHub Desktop Documentation
What is the difference between Git and GitHub? Find an answer here.
GitHub Desktop
If you have not already, download the GitHub Desktop application and install it on your computer.
GitHub.com
Follow these instructions and sign up for a free personal GitHub account. Note: Make a note of the email address you use when creating this account as well as the password.
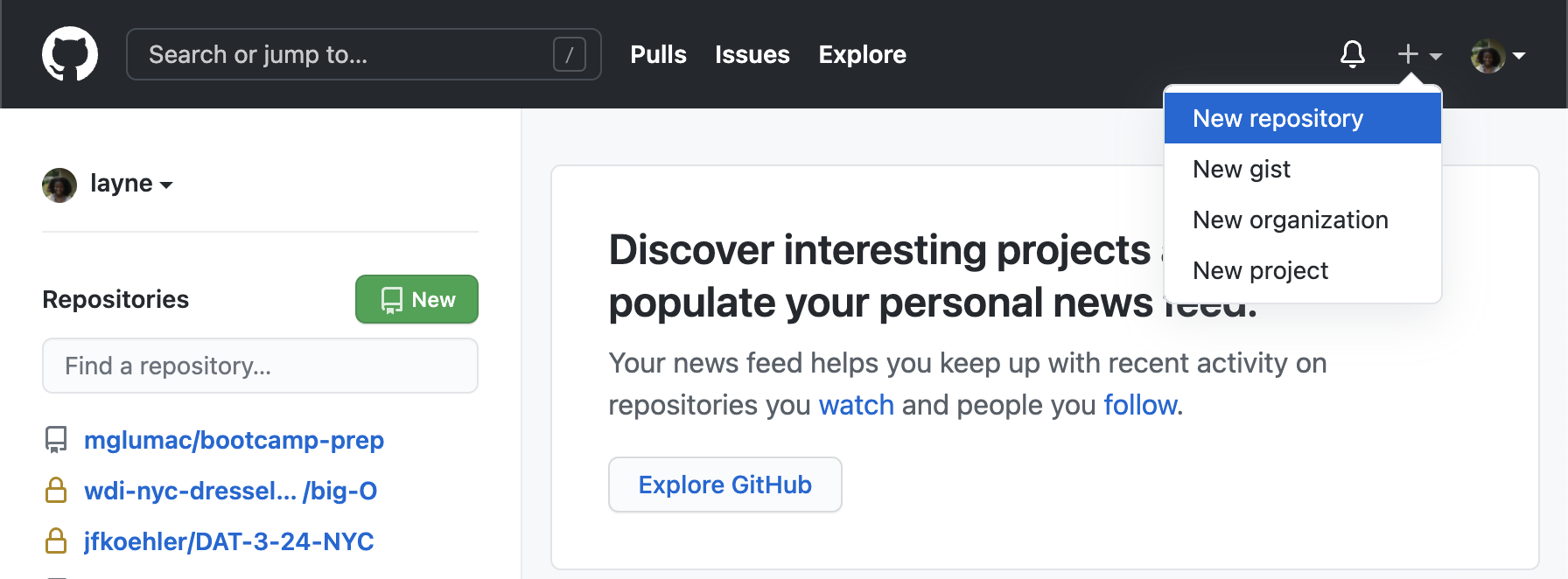
Create Repository
Log into github.com and create a new repository using the link under the + icon in the upper right of the GitHub homepage.
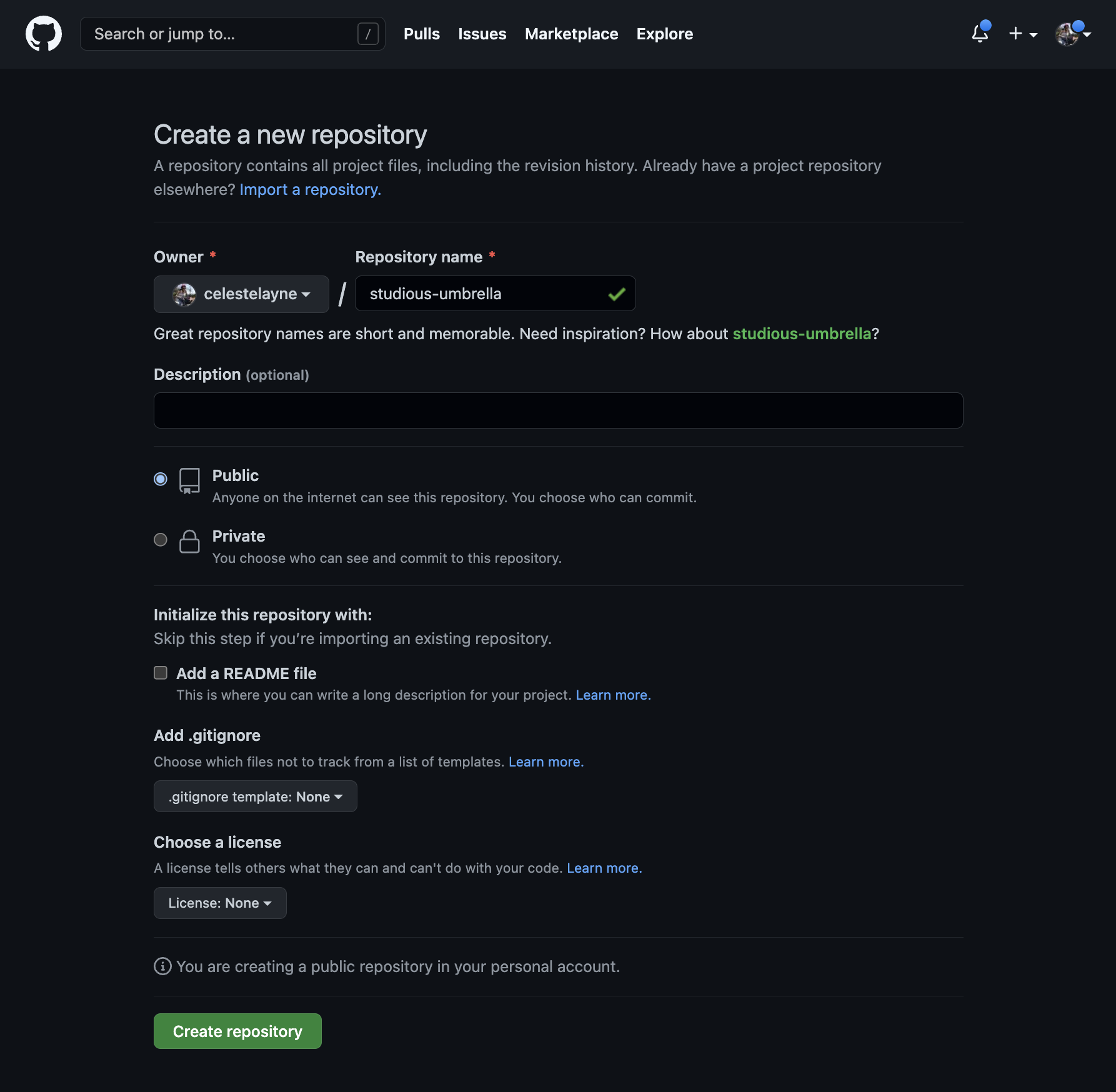
Name the repository. For example, I named this one studious-umbrella. Thanks for the recommendation, GitHub! Check the box to add a README file. This repository will be the home for the work produced in this module. Click the green create repository button.
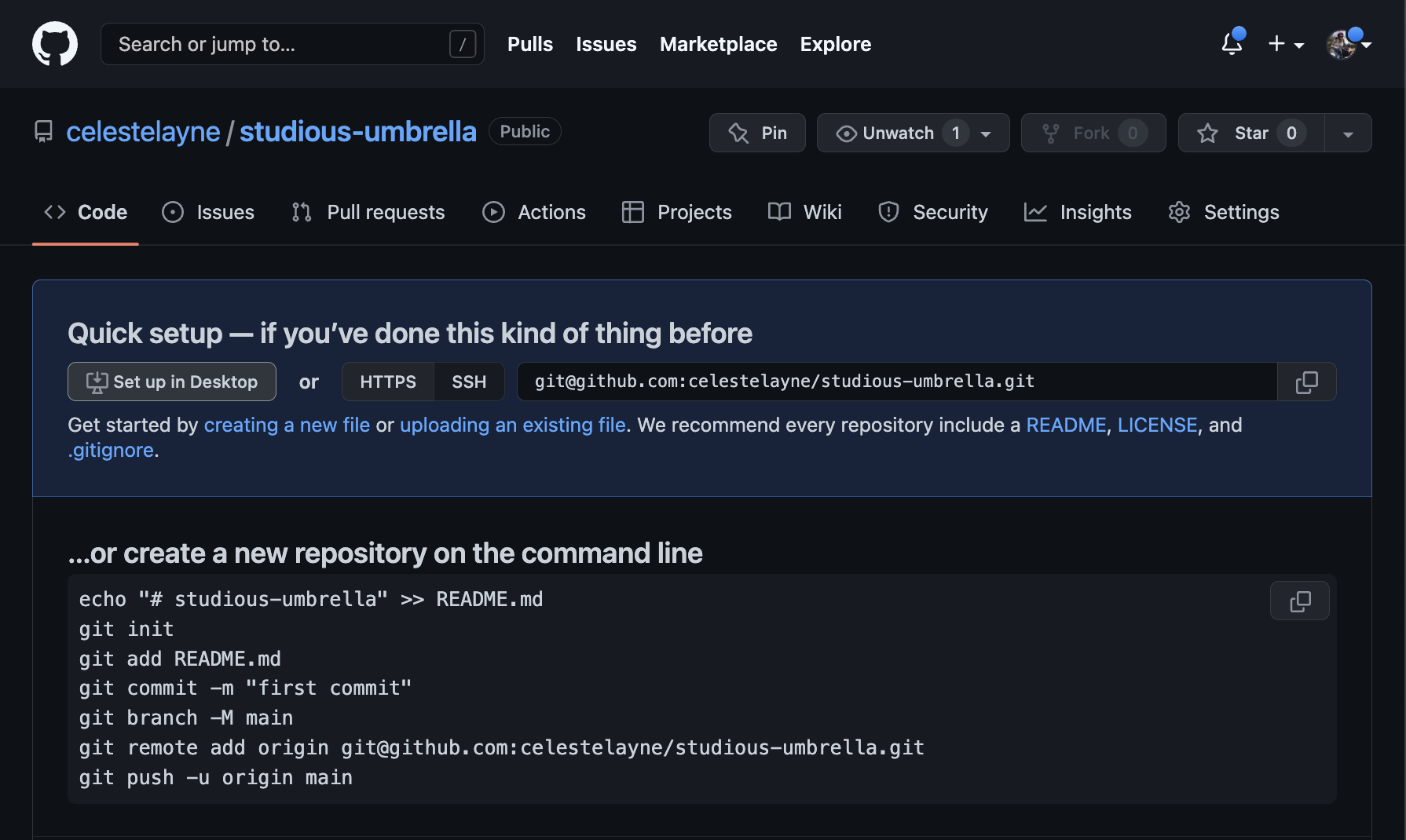
Once you’ve initialized the repository, it will take you to the home screen. Click the Set up in Desktop button.
When you press this button, you should see an alert window asking, Open GitHub Desktop? Click the Open GitHub Desktop button. This will launch the GitHub Desktop application.
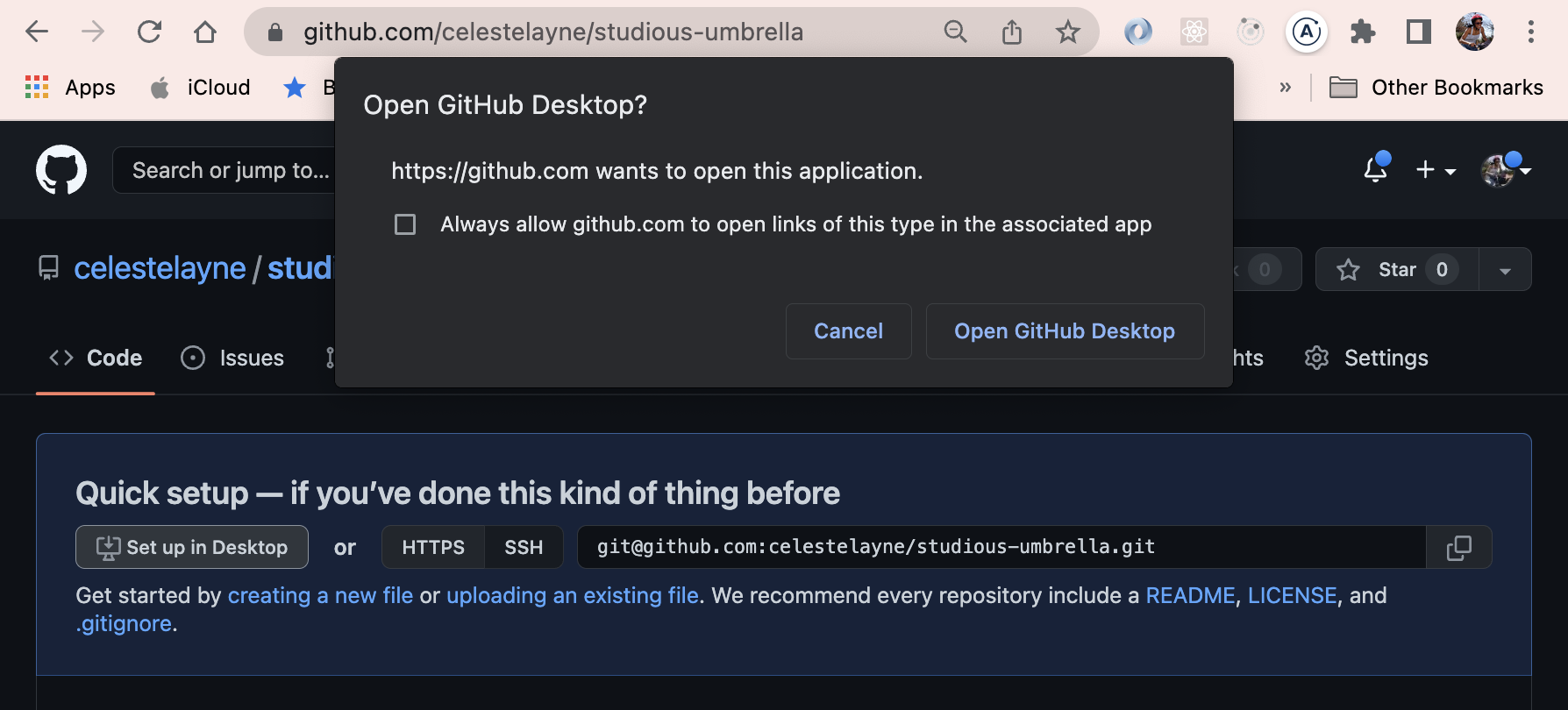
Now…(this is important) choose a place on your computer where you want this repository to live. You can do this by clicking on the Choose... button. My local path is: /Users/your-computer-name/Documents/GitHub/studious-umbrella. Once you've decideed where you want your files to live on your computer, Click the blue Clone button.
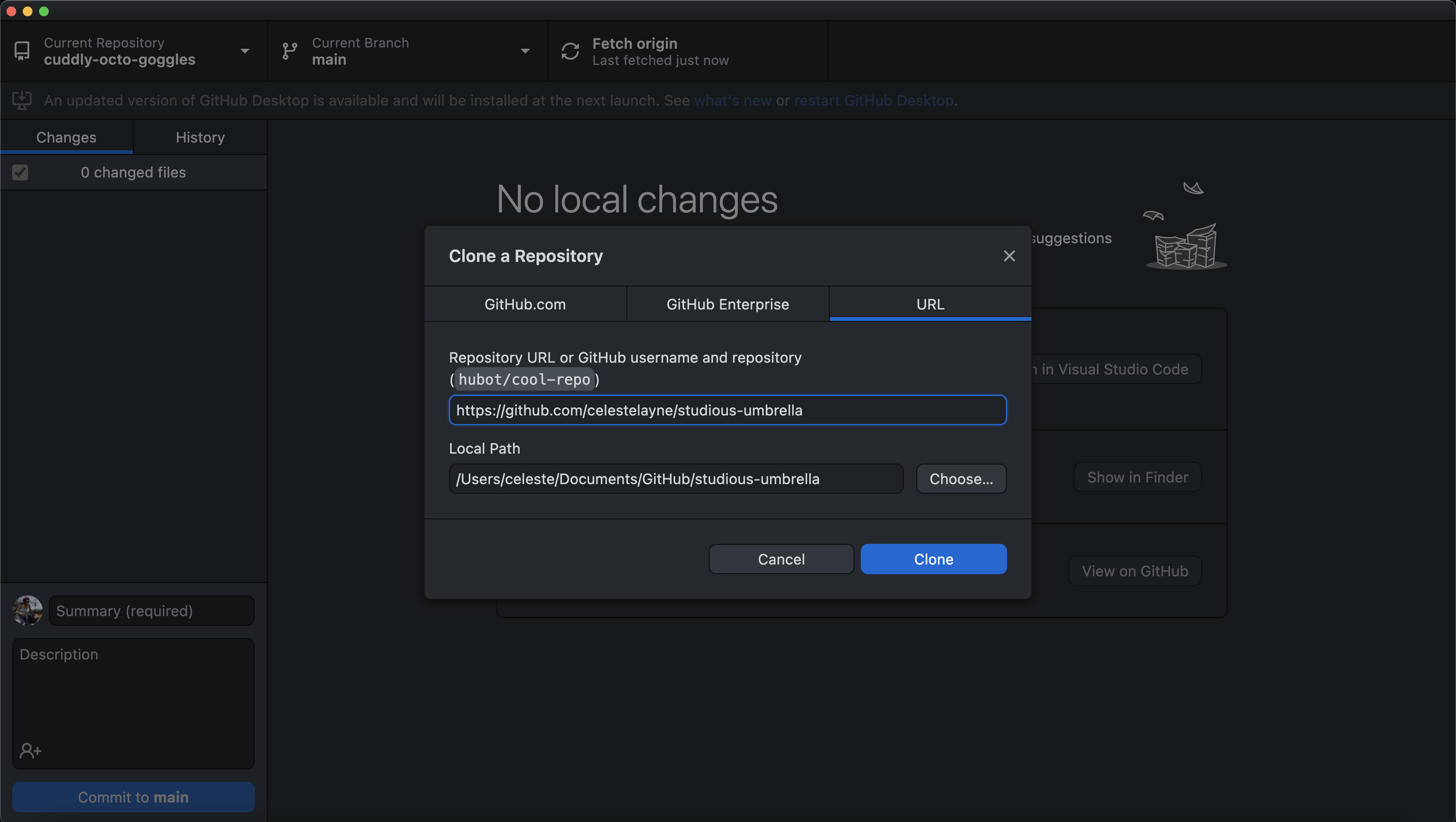
Yay! You’re in your local repository. GitHub Desktop provides some friendly suggestions for where to go next:
- Open the repository in your IDE (Visual Studio Code)
- View the files in the Finder on MacOS or File Explorer on Windows
- Open the repository page on GitHub in your web browser
If you select, Show in Finder, you will be taken to a folder named studious-umbrella, this is the local version of your GitHub repository. It’s local address is: /Users/your-computer-name/Documents/GitHub/studious-umbrella. We will use this as a space to archive the work in this tutorial.
Selecting Open in Visual Studio Code will immediately open the project folder, studious-umbrella in your code editor. You're ready to start coding!
Note: The name of the current repositiry (your project folder) in the top left screen.
Create Your First Webpage
See detailed instructions in the following document, Exercise 01: Hello World
- Open the repository in your code editor
- Make a new HTML file named
index.htmlin Visual Studio Code. - In Visual Studio Code, click on the
index.htmlfile which is currently blank and set up the bones for what will be your website by copying and pasting in the following code snippet, or using the one found here. - Modify the code with the words Hello World and save the file to your local GitHub repository.
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- your code goes in here -->
</body>
</html>
Push Local Code to Remote Repository
What is pushing?
Pushing is how you transfer your code from your local repository (the files on your computer) to a remote repository (the cloud, i.e. Github.com). What are we using to send your code to the cloud? GitHub Desktop.
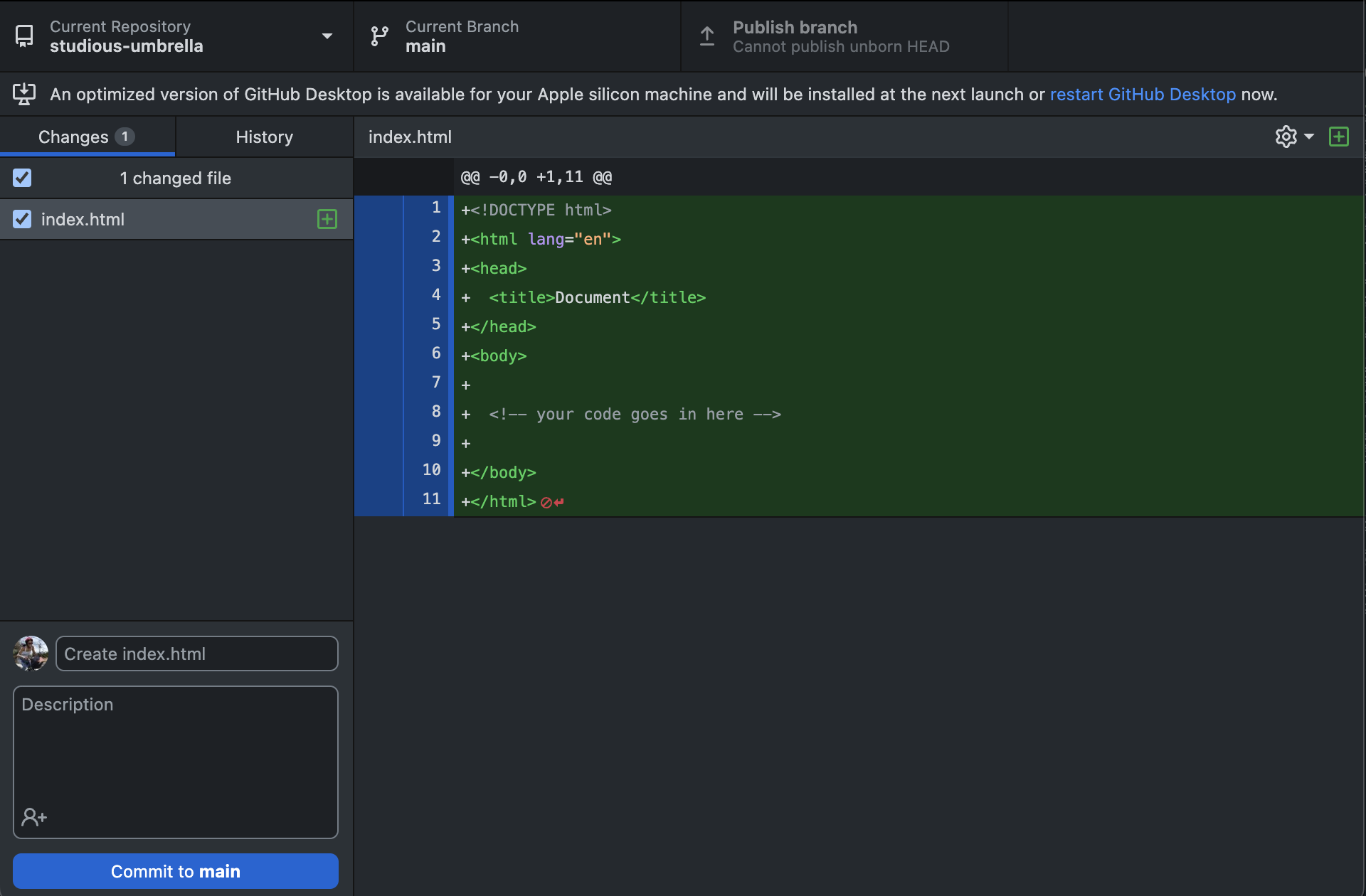
- Confirm that you see changes made to your file in the Changes Tab on the GitHub Desktop app.
- Above the blue
Commit to mainbutton you will see two form fields. You MUST fill out the top one. This is your commit message. It documents the changes that you've made to your code base over time. The description is optional, for now. - With the form filled in, click the blue
Commit to mainbutton, then the bluePublish branchbutton. - Now, check to make sure that your changes were pushed to the
maingithub.com repository (click on theView on GitHublink). Reload the GitHub.com page if you don’t immediately see your most recent changes.
Publish Your Website
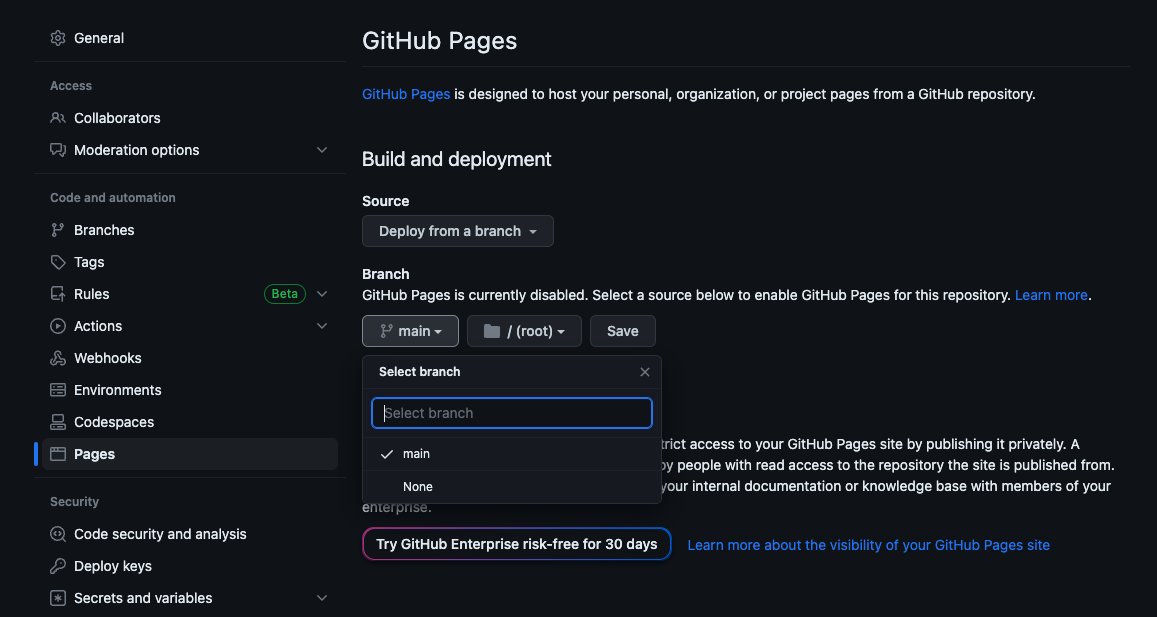
- In your github.com repository, find the
Settingstab in the top menu bar. - Scroll to the
Pagessection in the left menu. Under theBuild and Deploymentheading, click the dropdown menu under theBranchsub-heading and select themainbranch as your publishing source. Keep the/(root)folder for your publishing source. - Click Save.
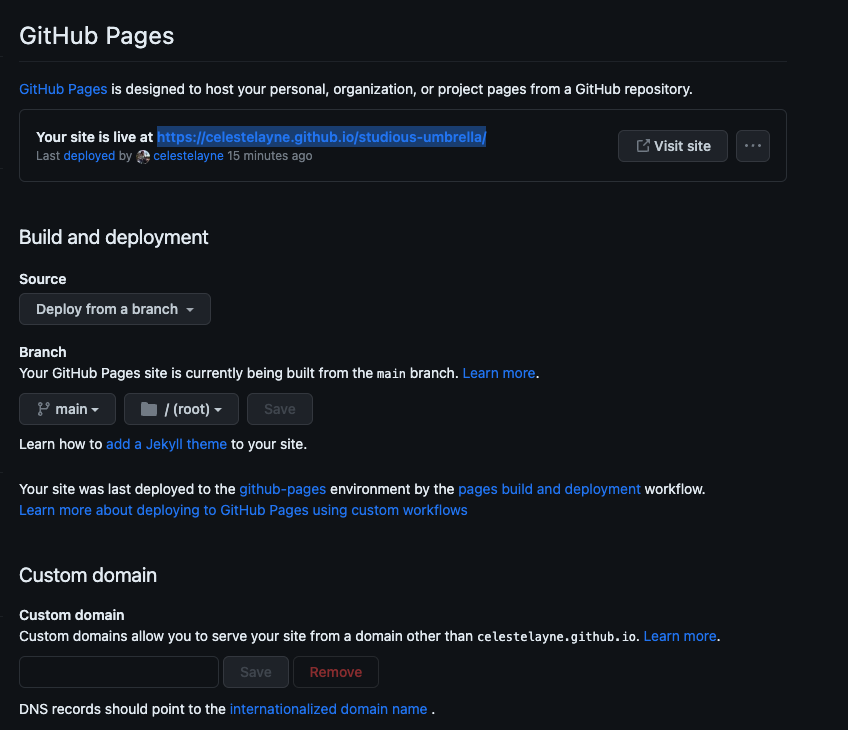
- Now, drumroll please! In the same GitHub Pages section, you should see a green success bar appear that says: "Your site is live at
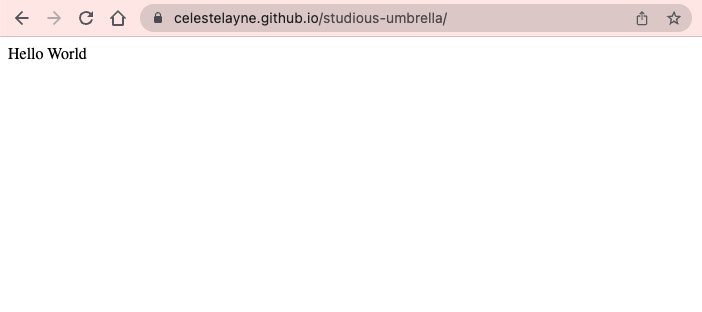
https://yourusername.github.io/studious-umbrella." Note: This may take a few minutes to occur. - Click on the link. Voila! Your site is live!
Challenge
Submit your website to this Google Form Interactive Web | Student GitHub Links. Please fill out all details.

